-
7 - 2. 행사 준비CS/ProblemSolving 2023. 9. 23. 15:03
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/30022
30022번: 행사 준비
첫째 줄에 정수 $N(2\le N\le 100,000)$과 정수 $A,B(1\le A,B\leq N;A+B=N)$가 공백으로 구분되어 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 $N$개의 줄에 정수 $p_i,q_i(1\le p_i,q_i\le 10^9)$가 공백으로 구분되어 주어진다. $p_i,q_i$는
www.acmicpc.net
그리디 문제중에 기본적이면서도 알면 좋을만한 기법을 쓸 수 있는 문제입니다.
행사 준비하는데 물품 N개가 필요하고, 이를 휴먼1이 A개 휴먼2가 B개를 준비하기로 합니다.
이때 상점 2개가 존재하는데, 각 상점은 물품 x, y, ...에 대해 서로 다른 가격으로 판매하고 있습니다.
이럴땐 담합 좀 하면 좀 좋아?행사에 필요한 물품은 각각 1개씩만 필요하기 때문에 두 사람이 가격을 비교해 각 상점에서 구매 했을때 최소 비용을 찾는 문제입니다.
최소 비용이기 때문에 여러가지 방법이 떠오를 수 있는데, N: 10만이고, A + B == N 이기 때문에 곱사건인 상황에서 해당 문제는 최대 [50_000][50_000]의 크기를 갖는 배열이 필요하므로, 가능한 방법이 많이 줄어듭니다.
금액 또한 최대 10억이니, 마땅한 방법은 그리디 밖에 없겠네요. (그래프를 직접 만들 수도 없고..)
그리디로 첫번째 떠오를 수 있는 방법은 A에 대해 정렬하고, B에 대해 정렬한 값을 비교해 최소 값을 뽑는 방법입니다.
코드는 아래와 같습니다.
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.*; public class Main { private static Pair[] products; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int B = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); products = new Pair[N]; for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); products[i] = new Pair(Long.parseLong(st.nextToken()), Long.parseLong(st.nextToken())); } Arrays.sort(products, Comparator.comparingLong(Pair::getA)); long left = leftMost(A); Arrays.sort(products, Comparator.comparingLong(Pair::getB)); long right = rightMost(B); System.out.println(Math.min(left, right)); } private static long leftMost(int count) { long answer = 0; for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) { answer += products[i].getA(); } for(int i = count; i < products.length; i++) { answer += products[i].getB(); } return answer; } private static long rightMost(int count) { long answer = 0; for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) { answer += products[i].getB(); } for(int i = count; i < products.length; i++) { answer += products[i].getA(); } return answer; } } class Pair { private final long a; private final long b; public Pair(long a, long b) { this.a = a; this.b = b; } public long getA() { return a; } public long getB() { return b; } }이와 같이 하는 경우 예제는 잘 돌아가겠으나, 반례가 존재합니다.
13이 정답이지만, 위의 코드는 14를 답으로 출력합니다.
5 2 3 1 1 2 2 2 3 4 4 4 5최소 비용으로 행사 준비를 해야한다는 특성을 잘 생각해봅시다.
즉, 어떤 물품을 살 때 매번 최적의 선택을 해야합니다. 여기서 최적의 선택은 어떻게 정의할 수 있을까요?
매번 어떤 물품을 고를때 얼마나 아낄 수 있었을까?라고 볼 수 있습니다.
위의 예제에서 우리가 A를 구매시 (4, 5)를 골랐을 때, B를 구매시 (4, 6)을 골라야 했다고 가정해보면, 최종적으로는 1원을 더 지불한게 되어버립니다.
이를 일반화 해보면, A구매시 (x1, y1)을 골랐을때 최종 y1-x1 만큼 손해를 본 것이고 전체적으로 계산하면 아래와 같습니다.
(x1, y1) (x2, y2) (x3, y3) ... (xn, yn) 의 물품이 존재할 때, A를 구매한 경우
x으로 구매한 총 비용
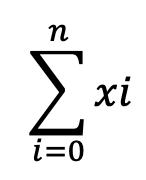
y를 샀다면, 절약할 수 있었던 총 비용
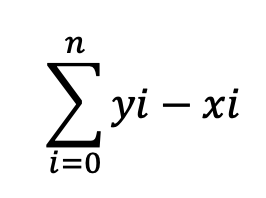
물론, B로 해도 상관은 없습니다. 수식이 조금 다르게 변화할 뿐..
어쨌든 이 케이스에서 우리가 최소 비용으로 구매할 수 있는 방법은 뭘까요?
x를 구매한 총 비용에서 가장 많이 아낄 수 있는 케이스를 찾으면 됩니다. >> 즉, 현 상태에서 절약할 수 있는 비용을 최대로 연산해주면 됩니다.
코드는 아래와 같습니다.
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.*; public class Main { private static long[] products; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int B = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); products = new long[N]; long total = 0; for (int i = 0; i < products.length; i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); long a = Long.parseLong(st.nextToken()); long b = Long.parseLong(st.nextToken()); total += a; products[i] = b - a; } Arrays.sort(products); for (int i = 0; i < B; i++) { total += products[i]; } System.out.println(total); } }반응형'CS > ProblemSolving' 카테고리의 다른 글
4 - 3. Xayahh-Rakann at Moloco (Hard) (0) 2023.03.11 4 - 2. Closing the Farm (Gold) (0) 2022.06.05 7 - 1. 우체국 (0) 2022.03.06 1 - 3. 공유기 설치 (0) 2022.01.18 9 - 1. Dijkstra 예제 (Parity Constraint Shortest Path) (0) 2021.02.01